DMEEA-WP1MS1.3-24W9
Key Achievements of this Week:(Working hours:50)
| Task | Time Investment | Status |
|---|---|---|
| 1st Year Annual Review | 35/40 | 87.5% |
| Carbon Calculation Training (City-level Database Provided) | 3/40 | 7.5% |
| Preparation of 4th Version of TSu BP | 2/40 | 5% |
| Personal Website Construction | 10 hours more | +25% |
Research Progress
The progress report focuses on multi-scale electrolysis energy system modeling,emphasizing two main areas: system level operational dynamics optimization using Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and cell level descriptor database analysis.
- Paper 1 : System Level
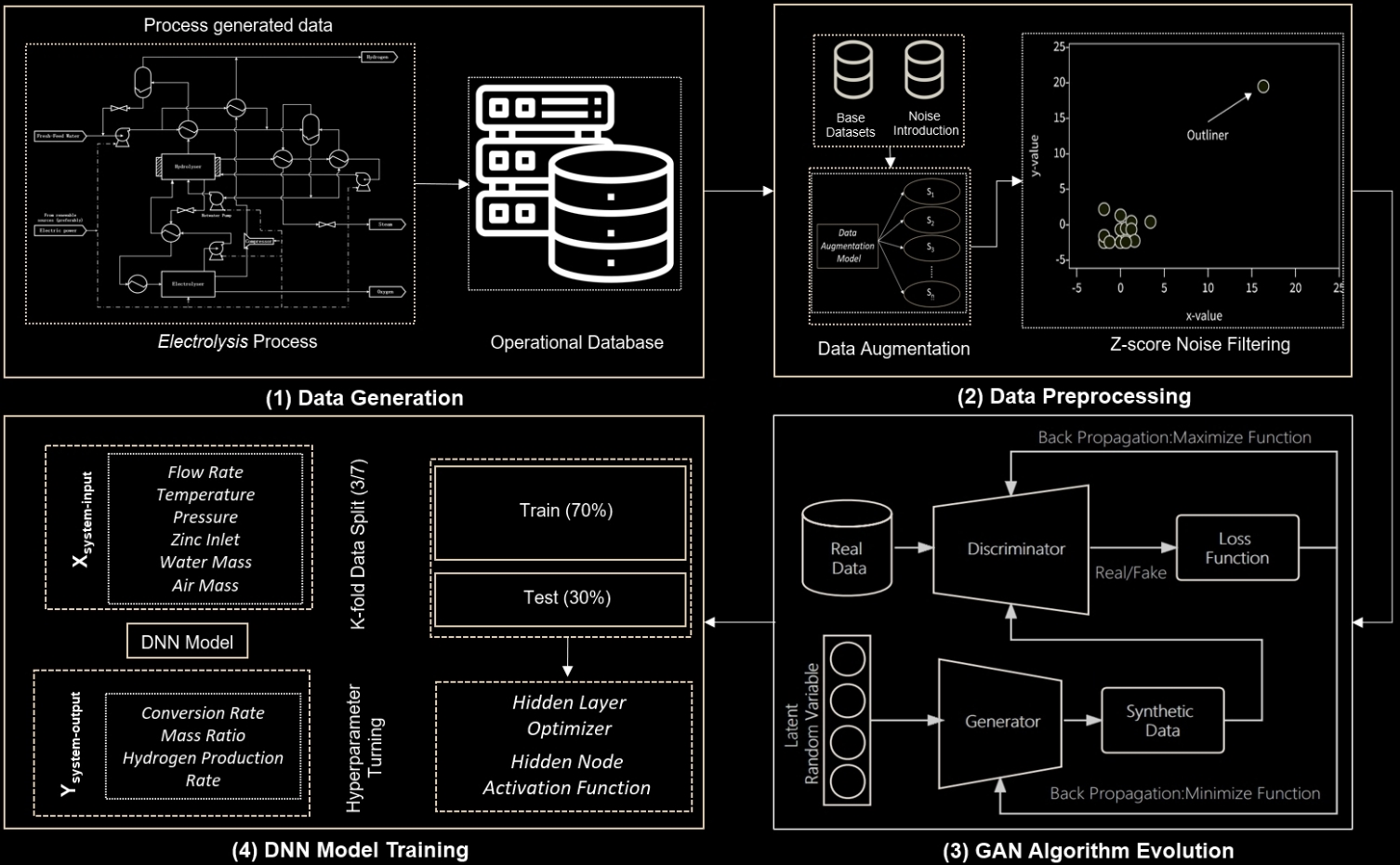
- The first part of Chapter 3 introduces an innovative approach to optimizing the operational dynamics of electrolysis energy systems using Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs). This section delves into the challenges of small dataset sizes in the field of renewable energy research, particularly in the context of electrolysis for hydrogen production. The researchers employed GANs to generate synthetic data, thus augmenting the existing datasets and overcoming the limitations imposed by scarce data. This process not only enhances the robustness of the model training but also preserves the statistical integrity of the original dataset, expanding it five-fold to over 2,000 data points. The preliminary evaluation of this synthetic data, conducted using a deep neural network (DNN) architecture, showed an increase in prediction accuracy, as evidenced by improvements in mean squared error (MSE) and R-squared (R²) metrics. This innovative approach signifies a leap forward in the predictive modeling of electrolysis system dynamics, paving the way for more efficient and reliable hydrogen production.
- Paper 1 : System Level
- Paper 2 : Component Level
- The second part of Chapter 3 focuses on the cell level descriptor database analysis for Proton Exchange Membrane Water Electrolysis (PEMWE). The section outlines the development of a comprehensive database aimed at reducing the power-specific cost and increasing the efficiency, reliability, and durability of PEMWE systems. By leveraging artificial intelligence and machine learning, the research introduces a novel method of data augmentation using GANs and Gaussian blur techniques to address the challenge of limited dataset sizes commonly encountered in laboratory settings. The database, consisting of over one thousand datasets and nearly forty thousand data points, allows for the prediction of membrane electrode assembly performance with remarkable accuracy. This approach not only enhances the understanding and optimization of PEMWEs but also exemplifies the potential of data science in revolutionizing renewable energy technologies.
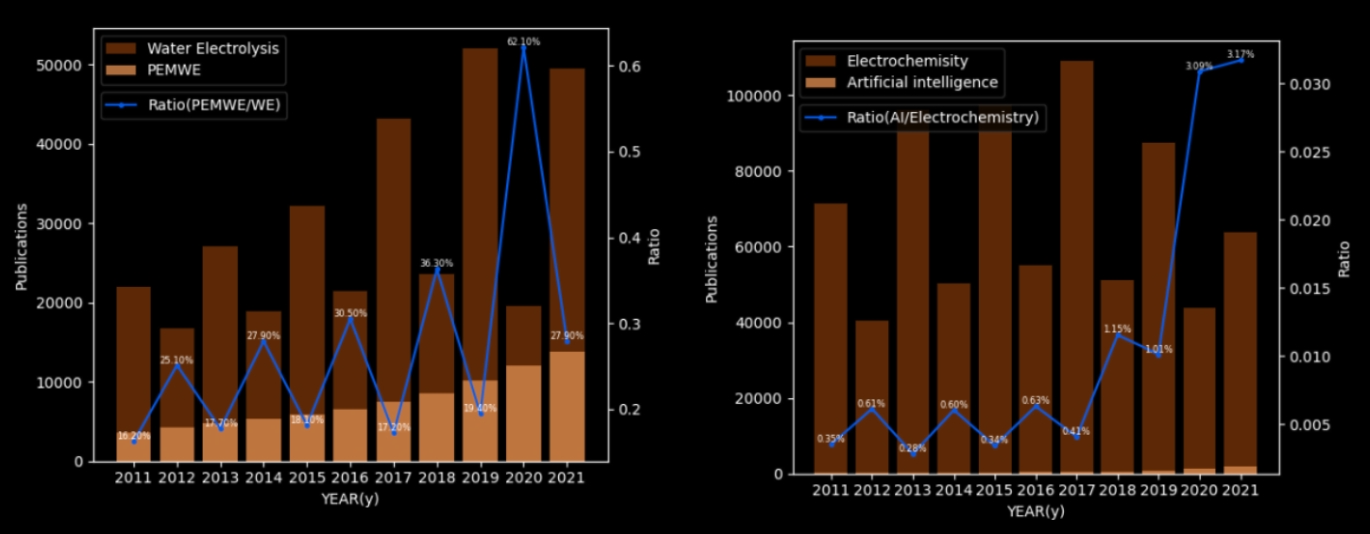
Background Literature Review Survey
Team Contribution
- Carbon Emission : Dataset Provided
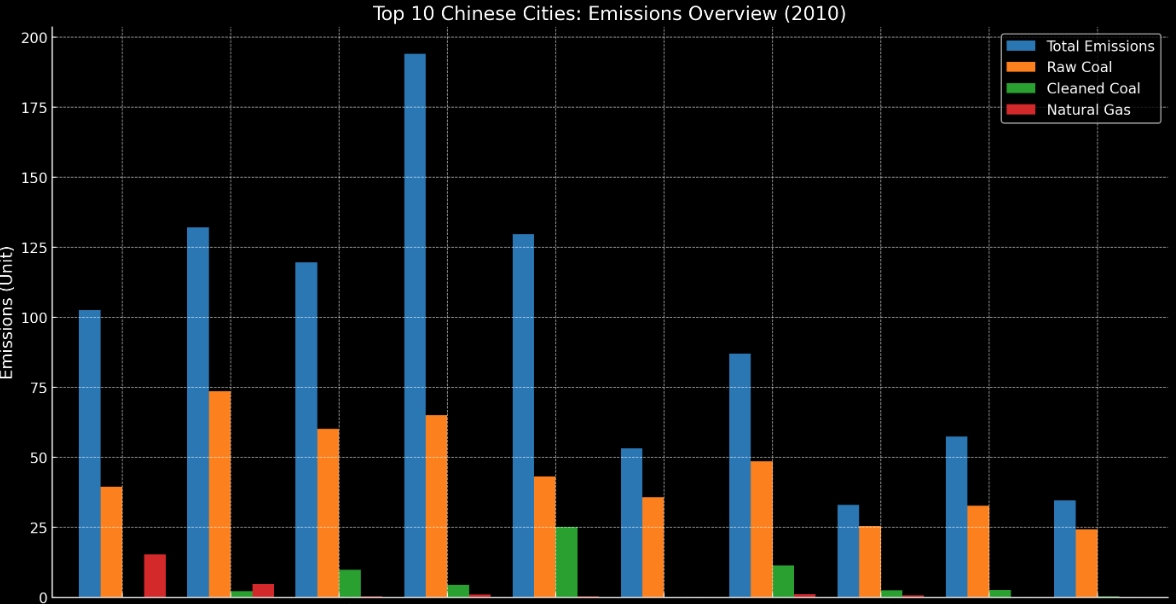
- Based on emissions data for 182 Chinese cities from 2010, I provided PhD student with datasets and algorithms for carbon calculation research. This mentorship, offering access to emissions data and analytical methods, aims to enhance their ability to conduct environmental assessments. This effort advances their research skills and contributes to understanding urban emissions, supporting effective carbon management and sustainability strategies.
- Carbon Emission : Dataset Provided
This Weeks’ Schedule (80 hours allocated)
- This Week’s Schedule
- Review and Finalize Paper 2(component level):
- Incorporate Findings from Recent Work to Paper 3(system level):
- Organize the formulas and data sources appearing in the fourth article
- This Month’s Outcome
- Annual Review
- Paper 2 Dataset Finalization
- This Quarterly’s Plan
- 1st Year Upgrade
- Paper 2 and 3 Finalization
- Paper 4 and 5 Proposal
- 2 Paper Abstract Review
- Progress Report and Business Plan
- 1 Conference Registration
This post is licensed by Haotian MA